In the following series we will look into the certificates in Kubernetes. In the first article we will focus on a freshly setup cluster with kubeadm and which certficates are installed where. The second article dives into creating certificates in the cluster so that you can authenticate with them. In the third we look into creating a own CA installing it on the host machine and then creating a cluster with it.
- Article 1 – Inspect the Cluster
- Article 2 – Add Ingress and API Gateway Certificates
- Article 3 – Authenticate with a Certificate
- Article 4 – Create a Cluster with your own CA
- Article 5 – External CA
Article 1 – Inspect the Cluster
Certificates are an integral part in computer science. From securing the connection between to hosts to some other stuff. In Kubernetes they are also very important. At first we look at a freshly setup Kubernetes Cluster (like shown in the Article here) which certificates are used. Then we look into trusting this certificate and in the last step we look into creating an own CA and assigin it to the Cluster.
Certificates in Kubernetes
Kubernetes has three important locations at which Certificates are stored, like shown in the picture below. The general Kubernetes certs are stored at /etc/kubernetes/pki, the certs fpr the etcd Database are at /etc/kubernetes/pki and the certificates for the kubelet are at /var/lib/kubelet/pki.
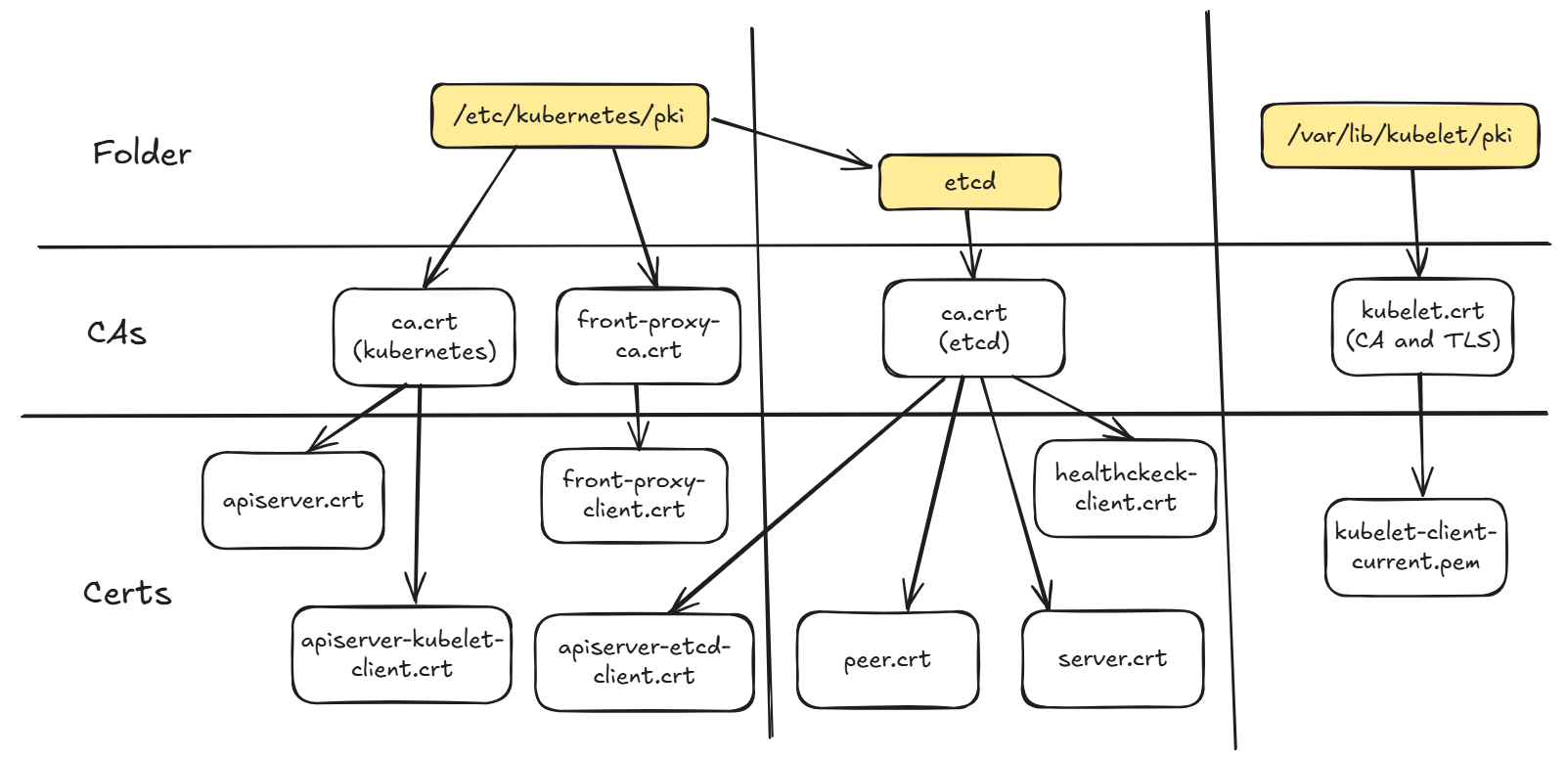
Certificates in Kubernetes
A certificate Authirity is an entity which issues certifiacates which then can later be used for securing communication like in the kubernetes cluster. In the case of kubernetes there are three present on the master node and one present on each worker. These are:
Master Node Only
- /etc/kubernetes/pki/ca.crt (main Kubernetes Certifiacate)
- /etc/kubernetes/pki/etcd/ca.crt (Securing etcd Communication)
Every Node and Master
- /var/lib/kubelet/pki/kubelet.crt (CA and cert bundeld)
In our case we will only look into the Kubernetes Certificate because this is relevant for the connection to the API server and the internal communication between the different components except.
Kubernetes Conf Files
To talk to the API Server and authoirze ourselft after the Kubernetes installation (Article here) it says you should copy the file from /etc/kubernetes/admin.conf to the ~/.kube/config file. This file contains a certificate which is signed by the Kubernetes CA and therefore is trusted by Kubernetes. If we look deeper into the /etc/kubernetes folder we find three more conf files which have different purposes:
- admin.conf (Default Kubernetes admin)
- super-admin.conf (Kubernetes admin which bypasses RBAC)
- scheduler.conf (Used by the Scheduler to authorize)
- controller-manager.conf (Used by the Controler Manager to authorize)
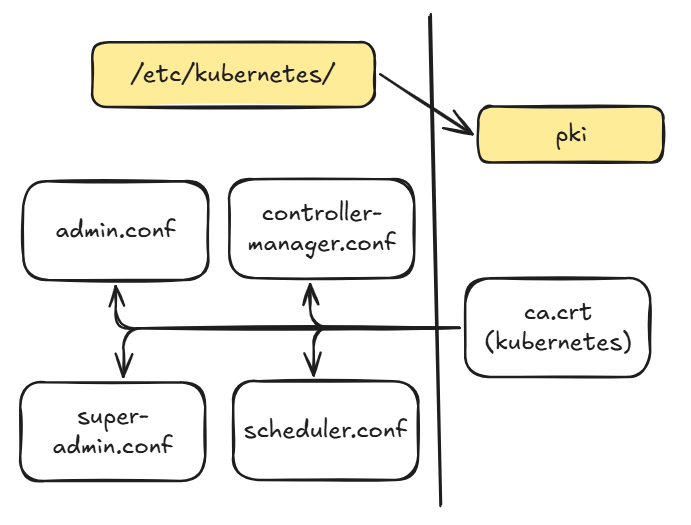
Analyze the Files
With the groundwork done we can now look deeper into these Certifiacates and inspect them more closely. To inspect Certifaicete in general we can use the powerfull openssl command. We will use this tool also in the next articels for creating our own CA and Certificates. At first we look into the Kubernetes CA.
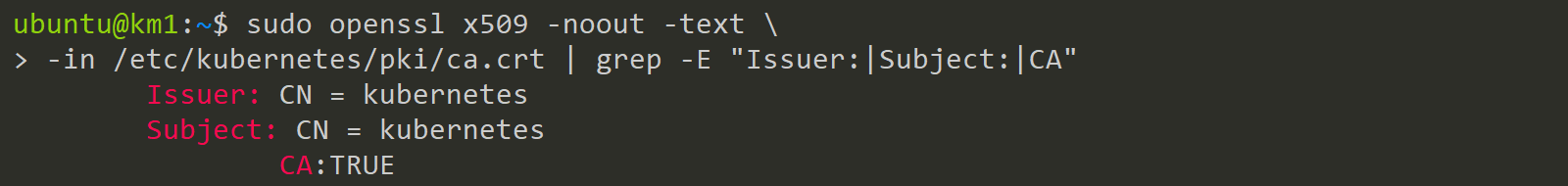
With the follwoing command we get a general overview of the Kubernetes CA file. The importend output is filtered with teh grep command. You can also ommit the grep and look at the whole output. In our case it is important for use to know, that this file has CA:true which means it can sign other certificates. A deeper explanation will follwo in the third article where we create our own CA.
sudo openssl x509 -noout -text \
-in /etc/kubernetes/pki/ca.crt | grep -E "Issuer:|Subject:|CA"
To check if the Signer of the Certificate and the certificate are the same we can use the issuer_hash and hash and if these two match, then it is selfsigned.
sudo openssl x509 -noout -hash -issuer_hash \
-in /etc/kubernetes/pki/ca.crt

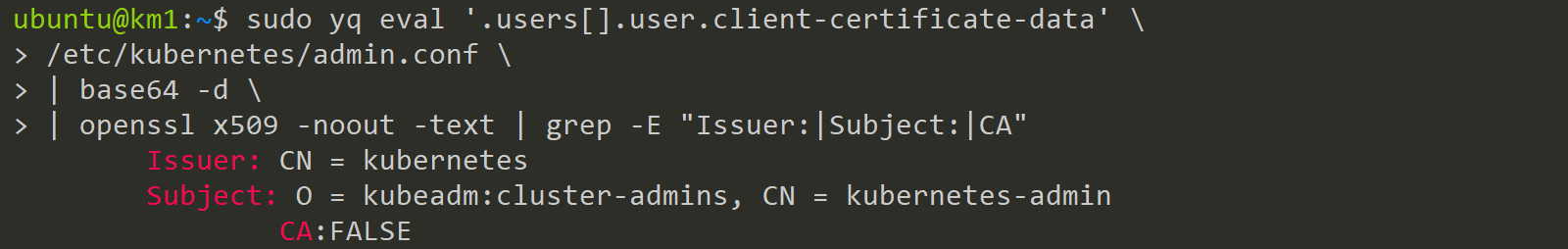
Now we look at the admin.conf an the Certifiacate in there.
sudo yq eval '.users[].user.client-certificate-data' \
/etc/kubernetes/admin.conf \
| base64 -d \
| openssl x509 -noout -text \
| grep -E "Issuer:|Subject:|CA"
sudo yq eval '.users[].user.client-certificate-data' \
/etc/kubernetes/admin.conf \
| base64 -d \
| openssl x509 -noout -issuer_hash
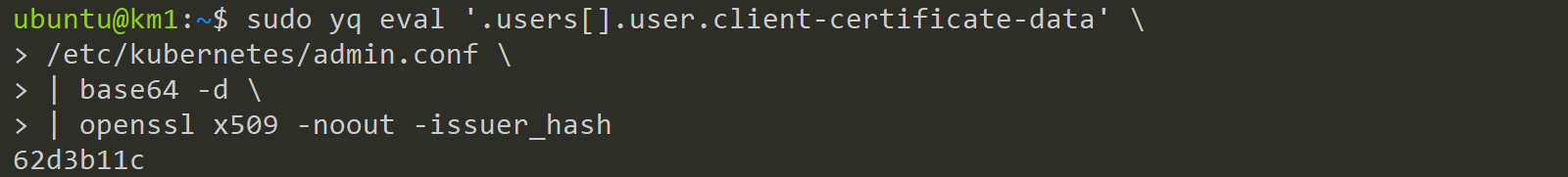
Now we analyze the Kubelet files.
openssl storeutl -noout -text -certs /var/lib/kubelet/pki/kubelet.crt
awk 'BEGIN {n=0;} /BEGIN/ "" { print > "cert-" n ".crt"} /END/ {n++}' < /var/lib/kubelet/pki/kubelet.cr
Kubeadm manage certifacates
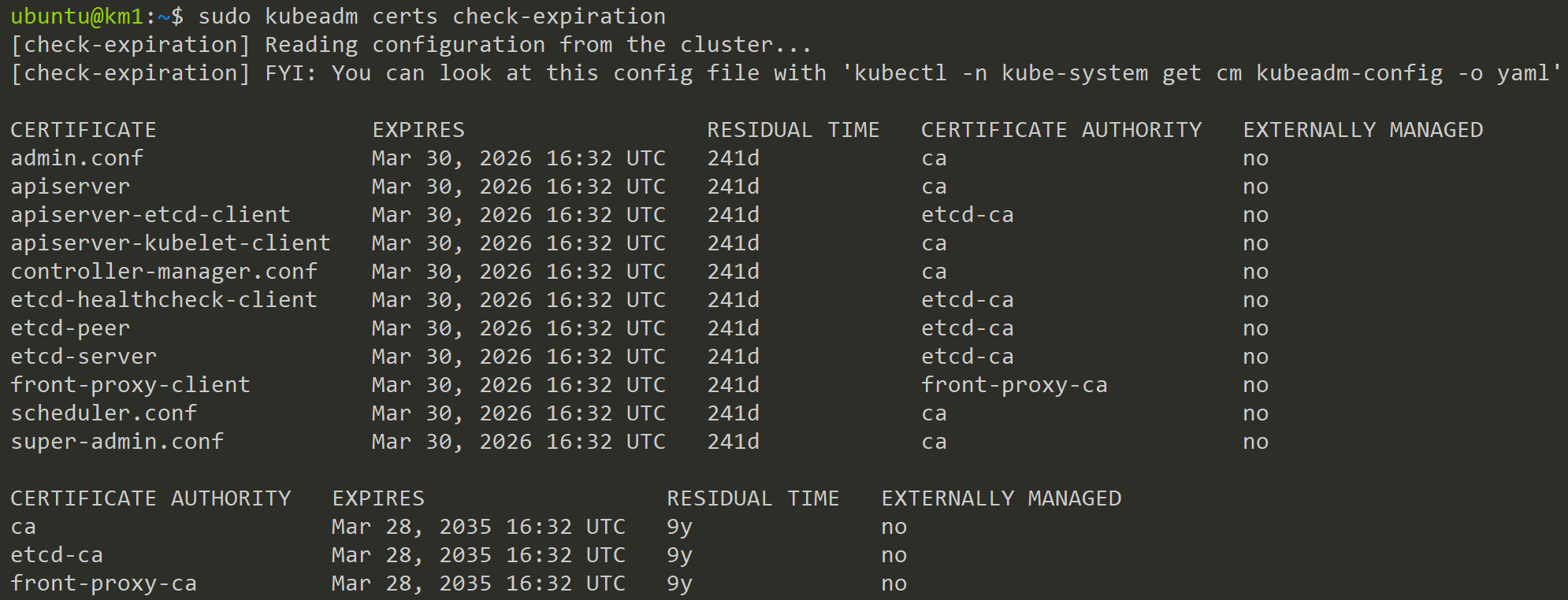
After an upgrade all certificates will be renewed
kubeadm certs renew all
https://kubernetes.io/docs/tasks/administer-cluster/kubeadm/kubeadm-certs/#automatic-certificate-renewal
Trust the Kubernetes CA
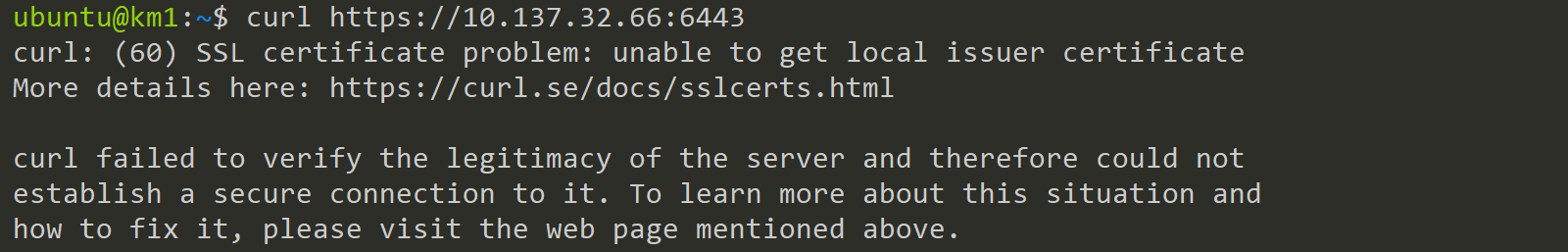
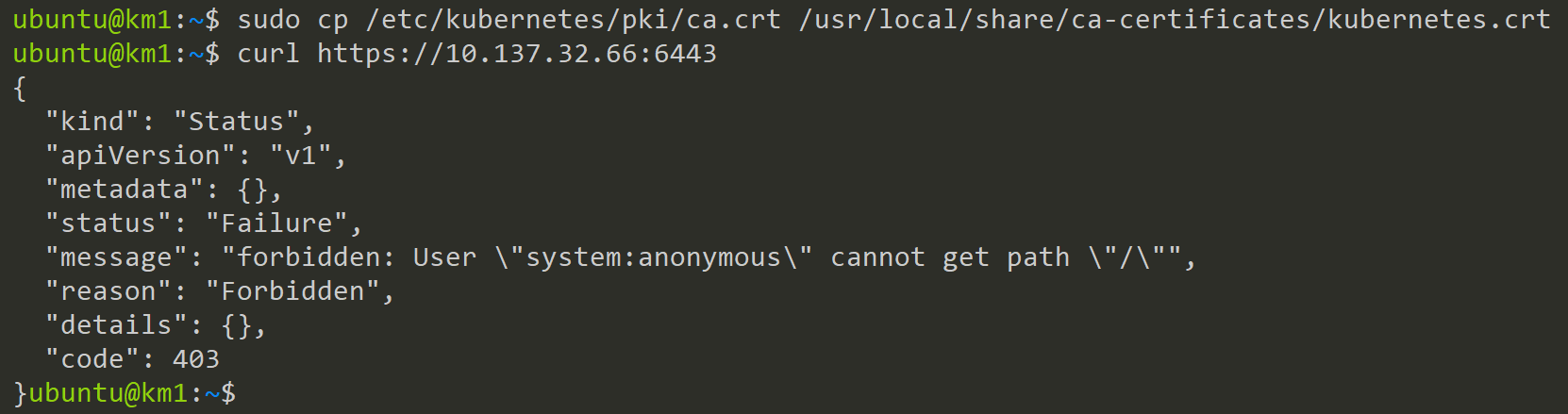
To trust this certificate need to put it into our trusted Certifacates. Ubuntu offers here two places:
- /usr/local/share/ca-certificates (automatically trusted)
- /usr/share/ca-certificates (manual selection)

Contact
For further questions contact me at: blog [@] dominiklandau.de
